Delivery & Shipping
How Do Maps Applications Work?
January 22, 2024 • 679 Views • 14 min read
Tetiana Stoyko
CTO & Co-Founder
Probably it is impossible to meet a single person, who doesn't know about Google Maps or its alternatives.
Various mobile apps with built-in map features have already become a significant part of our everyday lives.
We face them when looking for a taxi, ordering food delivery, parking locations, traffic jams, traveling to new places, planning our optimal routes, etc.
In summary, it is hard to imagine modern life without map applications.
So, is it possible to develop a custom map software solution, is such development even worth considering, what is the situation on the market, how to hire dedicated development team, and how do map apps work?
To answer all these questions, let's start from the very beginning.
What Maps Application Can Be Used For?
Cleary, maps existed long before their digital versions like Google Maps emerged.
There is no point in explaining the importance of such instruments because it is obvious. However, the importance of their digital variations might not be as obvious.
Clearly, such apps as Google Maps, for example, are providing the same features as traditional maps.
Truth be told, they are proposing even more options to choose from and are, in fact, much more capable and accurate, than their "ancestors".

For instance, software-based maps do not require any knowledge for successful use: most processes are already automated.
Starting with defining the exact location of the mobile device, and ending with extended location services like building numerous routes for outdoor navigation, they can also measure distances, predict arrival time, etc.
To cut a long story short, thanks to the software and algorithms, such apps as Google Maps have made navigation truly user-friendly.
They provide real-time updates and improvements, aimed at improving the user experience.
1.Food Delivery and Logistics
Another obvious conclusion is that such applications significantly impacted numerous industries, particularly delivery and logistics.
As a matter of fact, such software solutions have already become location-based technologies by default.
Such core features changed the entire industry of delivery, bringing countless options and possibilities, without which it is impossible to imagine such modern services.
Some such applications utilize the Google Maps platform in unpredictable and unobvious ways.
For instance, apart from parcel tracking, or choosing the destination point, as well as defining your current location, i.e. in what city you are, food delivery services are primarily location-based apps.
Thus, they also include your location to propose the nearest restaurants as a more preferred option to simplify and speed up the delivery.
Not to mention the overall impact of Google Maps navigation on the field of fleet management.
It allows to cut transportation expenses by route optimization and planning remarkably, real-time traffic updates, as well as the possibility to turn on the offline mode, in cases there is no satellite coverage in certain areas on the route.
And all the foregoing is just a small part of all the optional functionality available now in the industry.
2.Travelling and Entertainment
Last but not least, the Google Earth application brings prosperity not only to businesses and employees but also creates a lot of possibilities for regular citizens.
For example, Google Street View enables virtual tours all around the globe for everyone.
It proposes not only a map version of the world but also a 3D version of visual elements from countless places, caught on camera.
Finally, such instruments become essential for such new-age approaches as OSINT and GEOINT by allowing them to perform location intelligence.
For example, the Geoguessr game combines both, by making active users guess the random location from Google Earth or Street View, and find it on the map.
How Maps Software Works?
To cut a long story short, just like any other software, all mapping services are code-based.
Nevertheless, unlike the rest technologies, mapping applications require not only working lines of code but access to geospatial data.
Thus, all digital maps depend not only on the input information or the quality of the code but also on information about certain locations and areas.
For example, they use other maps and geospatial services, provided by third-party companies.
Apart from the already "traditional" digital look of mapping apps, it is also possible to turn on other map versions like satellite images, landscape visualization, etc.
These versions are optional for users, yet essential for the application owners.
In fact, all these types of data are required to make your mapping service as accurate as possible by comparing and contrasting all of the available data sources.
Alternatively, many such apps allow users to create their map layers.
They might include different information like public transportation maps overlaid in certain cities, or other possible marks.
Yet, in most cases, such maps won't be shared with all the active users, yet can be used for individual purposes.
To make it simple, location-based app development, as well as the creation of the map application itself is a very complex process.
It engages not only the software development but requires a lot of different types of data from various sources and highly depends on the work of third-party companies from other fields.
In other words, such a development task is extremely uncertain and expensive, requiring a large number of engaged and dedicated experts from numerous industries.
As a result, the number of digital mapping services is very limited. The most popular and influential examples of such technologies can be counted on fingers.
In addition to Google Maps, we can also name TomTom, Apple Maps, Waze, and Mapbox streets.
There are some other interesting mapping services with unique approaches like OpenStreetMap, which is based on the data, provided by its user community, instead of cooperation with various aerospace agencies. Yet, these are less famous and commonly used cases.
Google Maps Phenomenon
Fun fact: most modern location-based apps are using Google Maps API under the hood.
Plainly speaking, not all applications are using this particular technology. However, they might use Google Maps alternatives instead.
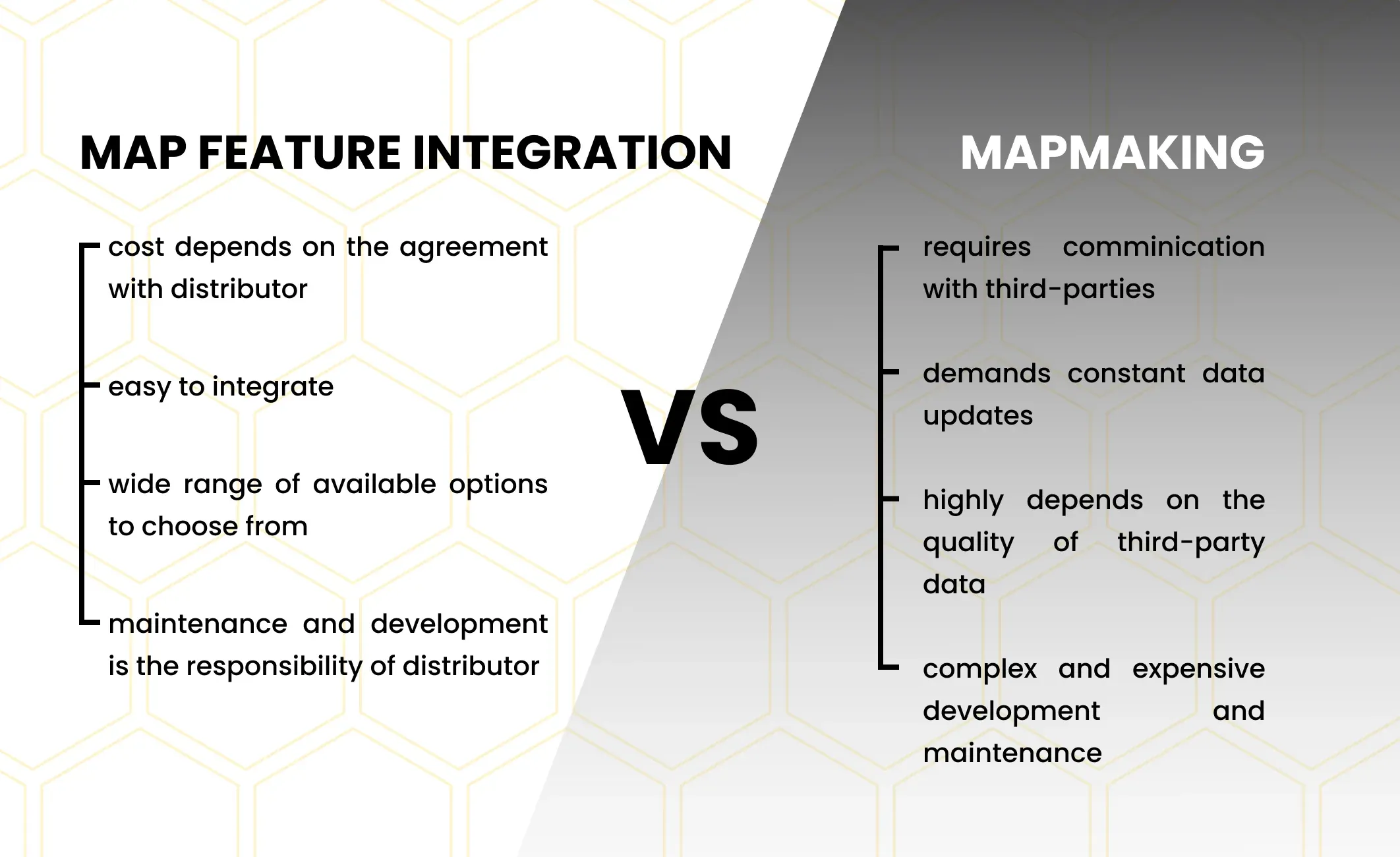
The reason is simple: it is much faster, cheaper, and easier to simply integrate a ready-made functionality and use SaaS software development solutions instead of developing custom ones.
As was said before, the main challenge is not the location-based app development, but the maintenance of the map feature.
In other words, a single feature will require as much effort and expense, as the whole standalone application.
The reason: it demands constant and incremental map updates, access to real-time data, experienced offshore software development team, etc.
There is no need to explain why it is unreasonable for small or even mid-size businesses because even such popular and huge corporations as Uber have to work with Google Maps.
They have tried to develop their own maps application for internal usage, but Uber had to give up this idea.
At least for now due to the high cost and extremely complex and resource-intensive processes, which are just the first step to developing a working full-fledge digital mapping service.
Therefore, there are so few global mapmakers, who are delivering maps as SaaS software development solution.
Such services make this functionality reachable both for regular active users and corporations, which require such software to achieve their business goals and perform their routine business activities.
Still, it doesn't mean, that there is a monopoly on this market or any other artificial restrictions and obstacles, which do not allow to become an active part of the mapmaking business.
The only actual issue is the overall complexity and final price for all the efforts and steps, required to be done to create a full-fledged standalone digital map application.
Instead, it seems easier and cheaper to simply use ready-made solutions, most of which are distributed as SaaS, via API, or even open-source projects, available for everyone for free.
As for now, Google Maps is the most common and popular SaaS software development solutions, which is constantly used in numerous software applications all over the globe.
Thanks to the popularity and recognition of the Google brand, as well as their access to limitless resources and huge active user community, it can gather even more data.
This makes the functionality of this and other mobile applications or services even more precise and accurate.
Is It Worth Developing a New Map Application?
The short answer is - no. It will be easier, cheaper, and faster to adopt one of the ready-made software products.
Nevertheless, for some reason, if you are not satisfied with this answer, there are a few steps to make a more informed and balanced choice on whether to adopt or develop on your own:
- Ask yourself about the purpose of developing your own map feature, and whether there are any crucial pros to developing a new project.
- Define the main reason for having this functionality: whether you are interested in creating a mapmaking business, that will be built around this feature, or are simply willing to enable it as an extra function option, that is beneficial for the business, yet is not a core technology.
Clearly, if you are willing to become a new digital maps distributor, you will need to create your own application with the related functionality, data gathering and analysis, etc.
In case, when your main goal is something other than building application maps like, let's say, the logistics industry, then it will be smarter and easier to find a ready-made solution, ready for integration.
Application Maps with Incora
One of the best ways to make a correct choice is to contact niche-experienced app developers for hire, who are familiar with such technologies.
For instance, our Incora remote software development team has some proven experience in working with map functionality, software development as a service, and white label app development which can be seen in our recent case studies.
Thus, if you struggle with choosing the correct approach to developing a map feature or a full-fledged map application - you can contact us in order to discuss your plans and ideas with our staff and find the most suitable approach to embodying your ideas.
What’s your impression after reading this?
Love it!
10
Valuable
2
Exciting
1
Unsatisfied
1
FAQ
Let us address your doubts and clarify key points from the article for better understanding.
How do maps applications determine my location?
Maps applications use a combination of technologies, including GPS (Global Positioning System), Wi-Fi, cellular network signals, and sometimes Bluetooth, to triangulate your device's location. GPS is the primary method for outdoor positioning, while Wi-Fi and cellular signals assist in more precise location determination, especially in urban areas.
What is GPS, and how does it work in maps applications?
GPS is a satellite-based navigation system that consists of a network of satellites orbiting Earth. Maps applications use signals from these satellites to calculate your device's precise location, speed, and elevation. A minimum of three satellites is needed to determine a 2D position (latitude and longitude), while four or more satellites are used for 3D positioning (including altitude).
How do maps applications provide real-time traffic information?
Maps applications use a combination of GPS data from users' devices and data from various sources, including government transportation agencies, to analyze traffic conditions. The apps then provide real-time traffic updates, suggesting alternate routes and estimated travel times based on the current traffic situation.
What are geocoding and reverse geocoding in maps applications?
Geocoding is the process of converting addresses (like "1600 Amphitheatre Parkway, Mountain View, CA") into geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude). Reverse geocoding, on the other hand, converts geographic coordinates into a human-readable address. Maps applications use these processes to display locations on the map and provide location-based information.
How do maps applications handle offline maps?
Many maps applications offer the ability to download maps for offline use. Users can download specific regions or areas when connected to the internet, and later use these maps without a data connection. This is useful for navigating in areas with poor or no network coverage.
How do maps applications update their maps and data?
Maps applications regularly update their maps and data to reflect changes in roads, buildings, and other geographic features. This data is sourced from various providers, including satellite imagery, government agencies, and user-contributed data. Users can also provide feedback to report inaccuracies or suggest updates.
What is augmented reality (AR) navigation in maps applications?
Some maps applications offer augmented reality navigation, where the camera on your device is used to overlay directional information on the real-world view. This helps users navigate by following on-screen directions superimposed onto the live camera feed, making it easier to understand directions in a real-world context.
How do maps applications protect user privacy and data?
Maps applications prioritize user privacy and often anonymize location data. Additionally, most applications allow users to control location-sharing settings and provide clear information about data collection practices in their privacy policies. It's important for users to review and adjust these settings based on their preferences.
Can maps applications be used for indoor navigation?
Some maps applications offer indoor navigation for large venues like airports, shopping malls, and museums. Indoor positioning technologies, such as Bluetooth beacons and Wi-Fi signals, are utilized to help users navigate within buildings where GPS signals may be limited.
Are maps applications available on different devices and platforms?
Yes, maps applications are widely available on various devices and platforms, including smartphones (iOS and Android), tablets, and desktop computers. Popular maps services include Google Maps, Apple Maps, and others, each with its unique features and capabilities.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
Let’s talk!
This site uses cookies to improve your user experience. Read our Privacy Policy
Accept
Share this article