FinTech
All about Smart Contracts: Use Cases, Security Measures, and More
November 25, 2022 • 251 Views • 17 min read
Tetiana Stoyko
CTO & Co-Founder
Smart Contracts can truly be considered a blockchain industry revolution. In fact, the modern crypto industry is probably among the most innovative and rapidly changing technologies. At first, this market provided us with cryptocurrency exchanges as an alternative FinTech trend, which turned the financial business sphere upside down.
Then, the blockchain gained popularity as well. As a result, the next service, related to this technology, known as NFT tokens appeared. Eventually, developers managed to create the «smart contracts» concept. So, what is so special about it and how can Smart contracts change our lives for good?
Briefly About Smart Contracts
Most regular users confuse Blockchain and Cryptocurrency because it is the most successful and popular blockchain use case. However, the blockchain is only a tool that helps to create cryptocurrencies, and it is not the only possible way to use it. To make it simple, blockchain is a way of storing and sharing data. The term itself consists of two independent words: «block» and «chain». They are crucial for understanding the main working principle of this tech. It stores data in blocks, each of which has its own capacity. When the data block is «full», it is connected with other blocks. A few blocks, connected with each other are known as chains. In other words, blockchain solutions store and transfer information about the transaction or other specific data in their own secure way.
Actually, the number of security measures varies, depending on the architectural approach and methods used for their development. For instance, most blockchains secure the data transaction by requiring approval from previously generated blocks. As a result, before «attaching» the new data unit, the chain gains approval from previous ones, checking if the new data is corresponding with previously saved data. If it is right, then the new block is «attached», and the new one is being formatted. Then, the process repeats until the final block is formed and approved.). Clearly, it is an oversimplified explanation of one of the blockchain's internal security measures and working processes.
Mostly, Smart contacts are operated in the same way. However, unlike cryptocurrency, they have slightly different requirements for the transferring and treatment process. Thus, while cryptocurrency ensures that the transaction is secure and constant, without interruptions, smart contacts are based on completely different principles and are used for other purposes. To Avoid unneeded complexity, the architecture of smart contract execution can be described as «if/when action A happens, then action B proceeds». In other words, they are based on the gradualness principle. As a result, this technology can be used to automate the bureaucracy in paperless processes.
Moreover, as well as any other blockchain-based technology, smart contracts are decentralized. Thus, in addition to the automation of various bureaucratic processes, they help to avoid contact with various third parties and middleman agents. Instead, the communication within the contract will be similar to person-to-person. For instance, both sides agree on the terms of the project, then create the digital contract, and start the working process. Hence, each of them could easily track the task progress, or ignore monitoring, and rather fulfill their obligations. Anyway, if the project meets the previously agreed terms and requirements, the self-executing contract event takes place.
Summing up in simple words, smart contacts are the new generation of paperless projects. To be more precise - the related agreements, terms, and other bureaucratic aspects. The main advantage of this generation is their capability to automate various processes, track the fulfillment of agreed requirements, and self-execution. Despite these advantages may seem primitive and rather a bonus, than must-have features, at least at the first glance, they can really simplify numerous routine activities, saving time and resources. To better illustrate this statement, let’s consider some features of this technology in more detail.
Advantages of Smart Contracts
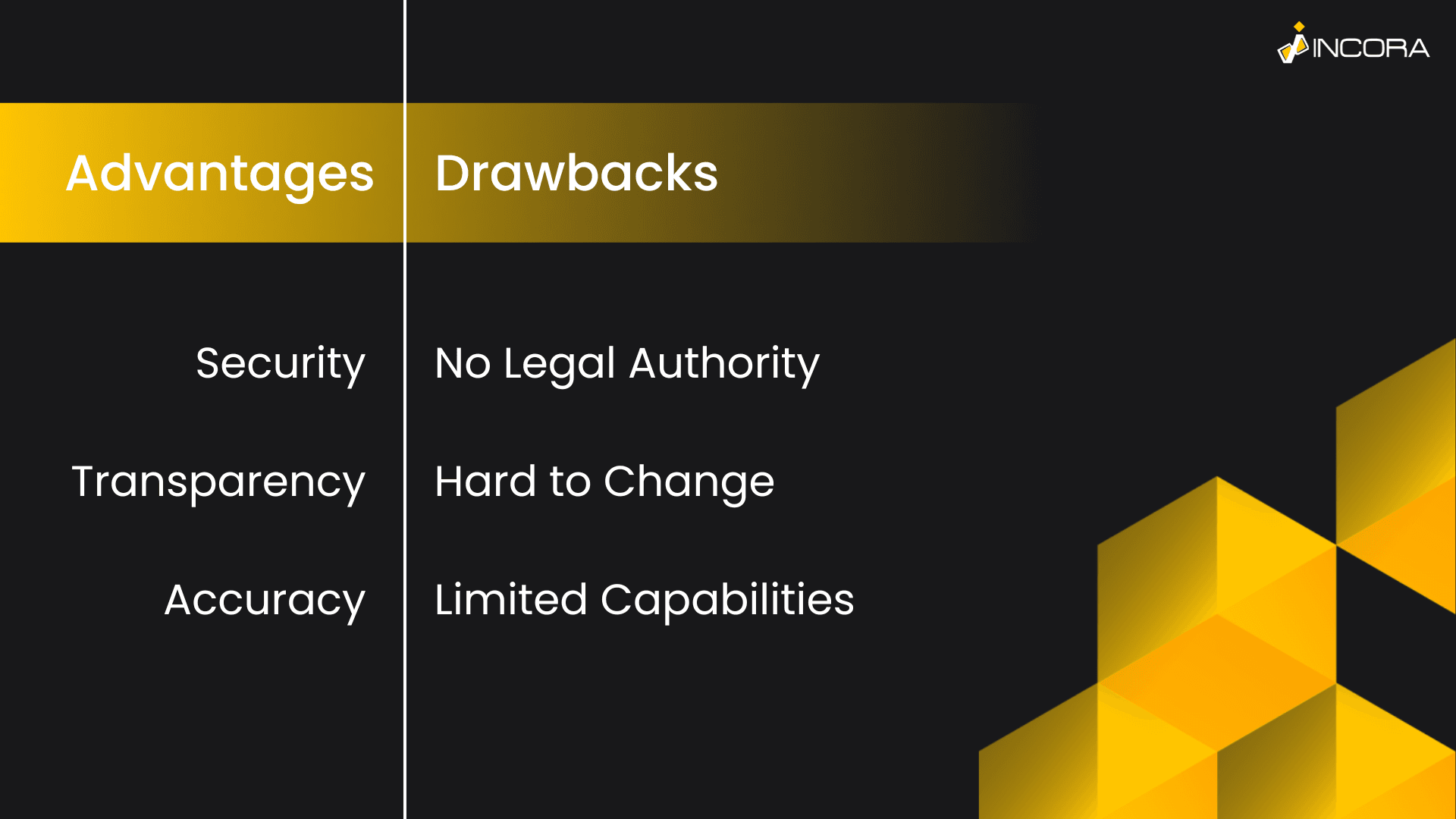
High Level of Security
As we previously mentioned, as well as any other product, based on blockchain networks, smart contracts development is very secure. For instance, it is impossible to make any unauthorized injections or changes. The contract data updates are guaranteed to perform independently, and in the way, they were agreed upon and designed to behave. In other words, it is very unlikely that they can be interrupted or their content will be replaced halfway through. Moreover, even if changes will be somehow implemented, it is impossible to make them secretly.
Transparency
The second feature of smart contracts, which also migrated from blockchain technology is transparency. It is the feature that guarantees that all the changes or transactions performed will be easy to notice. Also, it allows the creation of fair and clear agreement conditions. As a result, it will be easy to track the execution progress, or contract terms.
Precise Work
Eventually, smart contract development is based on computer algorithms. To make it simple, they are operated by the system. Clearly, this helps to achieve much more precise results. Contrary to humans, they rarely make mistakes. Of course, only if smart contract developers configured the system correctly. If smart contract developers did make mistakes during setting up the software, smart contracts can behave unpredictably. Yet, when we are talking about calculation, monitoring, or other strict processes, we have to admit that computing programs are more reliable.
Smart Contracts Drawbacks
Automation of Processes
Process automation is one of the most important and well-known features of Smart contracts. Frankly, we have already explained the main aspects of this advantage, thus let’s shortly sum it up. Smart contracts support the automation of various processes, which results in faster and more convenient document management. Yet, we didn’t note that despite the fact that this fintech trend aims to limit the bureaucratic aspects of the working process, they are incapable of getting rid of them. The same is true for third parties. In simple words, if the project requires the involvement of lawyers, they have to be involved. It is important to understand that smart contracts are just improving and simplifying the document management process, not performing it by themselves.
Hard to Change Terms
Frankly speaking, this specific drawback can be a real deal-breaker. It means that it is almost impossible to make any changes to the contract. So, if the deal was changed, most likely, you will have to create a new contract instead of changing the previous one. Thus, smart contracts are not the best solution for projects, where terms are regularly changing. Clearly, new smart contract development requires additional resources, finances, and time delay. Yet, this drawback is mostly related only to short-term estimations and agile projects. In other words, if you are designing a complex and strict development plan then you won’t struggle with smart contracts.
No Legal Authority
Also, we have to admit the fact that for now, Smart Contracts have no actual legal power in most countries. Thus, it is impossible to use them as evidence or a full-fledged legal document. Modern trends show that in the nearest future all blockchain-based technologies will most likely be regulated and, as a result, will be recognized by the state. However, right now they have no legal status.
Thus, once again, you won’t fully avoid contacting third parties like lawyers. The easiest way to cover this drawback is simply to create an actual notarized traditional contract. Therefore, it can be used to ensure that each side is fulfilling its part of a deal.
Clearly, Smart Contract would be much more preferable and standalone. Nonetheless, we have to be realistic and aware of all capabilities of such fintech trends. Still, they propose a unique service for checking the progress of the development and securely sharing data in real-time. There are simply no other alternatives, especially when we talk about paper-based contracts.
Limited Software Capabilities
Finally, smart contacts are a raw technology and have their own technical limitations as well. For instance, they can struggle with too complex coding, which is hard to understand for the machine. To be short, the unclear and messy code may create additional unneeded issues.
On the flip side, this will encourage the developers to keep their code clean and obvious. Another of these limitations is that it will be much easier for the testers to hunt the bugs and check the overall quality of the product. After implementing smart contracts into your project, your developers will be forced to achieve at least the minimum quality bar.
Use Cases for Smart Contracts
When it comes to smart contracts use cases, it is possible to find a 1001 solution on the web. Frankly speaking, most of these examples are far from being real practical usage examples. As we stated before, Smart Contracts are a recent and raw technology with all the related drawbacks. Also, they have no legal recognition. So, all these examples, when smart contracts can be used in various processes, which are highly related to the Law, are simply mistaken.
Clearly, you can transfer data or agreements via the blockchain. Yet, don’t be surprised, eventually, they will be proclaimed fake or useless. Therefore, we do not encourage you to use Smart Contracts for valuable or important contracts, associated with strict bureaucratic documents and processes.
Talking about more realistic use cases for Smart Contracts, we have to understand that they are in fact a way of transferring data, which is based on the “if/when … then” principle. So, if we will oversimplify, it is an automated and ordered way of transferring the data between various participants, which is performed according to the preset circumstances. As a result, it is obvious that there is a wide range of possible usage purposes. Yet, we will name a few of them just to better illustrate how it can work.
Group Decision Making
One of the best examples of smart contract implementation is to use them for decision-making in cases when a decision is being made by a group of people. So, it is possible to set the needed conditions like the right of veto, required 50%+ votes for or against the decision, etc.
As a result, any decision will be clear and trustworthy, allowing participants to make them at a distance and being sure they are correct and secure. There are no limits for such useful purposes, yet we can assume that in the nearest future, after recognizing Smart contracts at the level of the law, they can become an alternative to the traditional voting methods during the election campaign, or within the governmental structures.
Logistics and Shipment Industry
Probably all the best real-world examples of smart contracts are related to this sphere. It allows data sharing automation and better monitoring of the overall location or conditions of the goods. Moreover, today smart contracts are actively implemented in these industries.
For example, VeChain is creating a platform, based on blockchain technologies and smart contracts, for shipment companies. With the use of third-party hardware and software, connected to the supply chain, they propose a wide variety of useful features like the temperature storing status of the shipment. Including the fact, that blockchain is a way of storing and sharing data in a secure and fast way, we get a fast, secure and reliable way of communicating and informing, which is clearly a great bonus for such industries.
How to Create Smart Contracts in Blockchain
Actually, the creation process is relatively regular and easy. First of all, you need to plan your smart contract. To be more specific, choose the best blockchain for smart contracts, figure out your tech stack, plan your actions to be done, etc. Honestly, among the best blockchains for smart contracts is Ethereum. It is also the most preferable among the developers due to the fact, that there are numerous solutions for such purposes.
Frankly, it is possible to list all steps on how to create smart contracts in blockchain in a simple scheme:
- Plan and choose the instruments.
- Connect to the Ethereum blockchain network via third parties.
- Create an App and API.
- Create an ETH account and add ether.
- Create a project.
- Connect all components.
- Compile the contract.
- Deploy it.
Clearly, the scheme does not show all the processes. In fact, the development of smart contracts is a complex and demanding procedure. Its full and detailed implementation tutorial is worth a standalone article due to the fact, that it is a very large-scale activity.
End Line
Real-world examples of smart contracts indeed are a sample of revolutionary technology, which can become a game-changer once. Yet, at the moment it is rather a prototype with a limited number of potential use purposes. Nonetheless, it doesn’t mean, that it is not worth your attention. Conversely, it is better to start considering and developing it now. Thus, in the future, you will have an advantage over your possible competitors. In order to better understand the conditions for the Smart Contract implementation, we propose you examine some case studies.
What’s your impression after reading this?
Love it!
1
Valuable
1
Exciting
1
Unsatisfied
1
FAQ
Let us address your doubts and clarify key points from the article for better understanding.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
Let's talk!
This site uses cookies to improve your user experience. Read our Privacy Policy
Accept
Share this article